Non-invasive investigation of microplastics in soil
Project description:
The continuous input of microplastics changes the conditions in the soil habitat and affects soil biota. However, our understanding of how microplastics alters the structure and functioning of soil is still very limited. Typically, destructive methods are used for analysing microplastics in soil, which means that valuable information about the structure of the soil sample is lost.
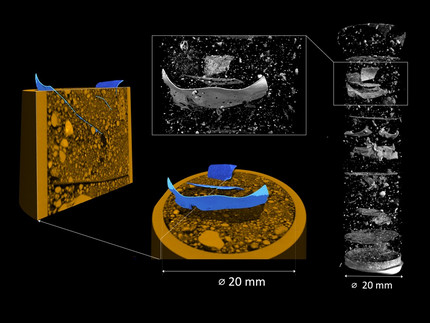
We use a non-invasive combined imaging approach of neutron and X-ray tomography which allows us to determine the position, shape, and size of the microplastic particles and simultaneously analyze the three-dimensional structure of the surrounding soil matrix. In this project, this novel methodological approach will be tested, optimized and then applied to better understand how microplastics of different size and shape affect soil microstructure and properties. Tötzke et al. 2024
Contact: