Biosynthesis of nonribosomal and ribosomal peptides in cyanobacteria
Background
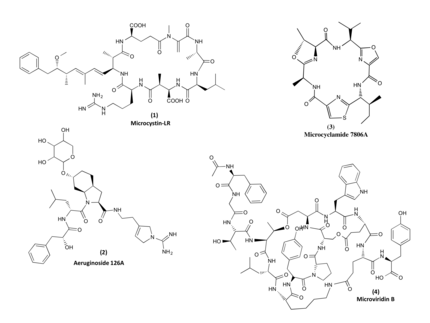
Cyanobacteria are increasingly recognized as prolific producers of natural products exhibiting unique structural features as well as showing potent bioactivities. Investigations into the biochemistry responsible for the formation of these compounds have revealed fascinating mechanisms that are not, or only rarely, found in other microorganisms. Many of the compounds have a peptide backbone comprising a multitude of non-canonical amino acids and featuring different types of macrocyclizations.
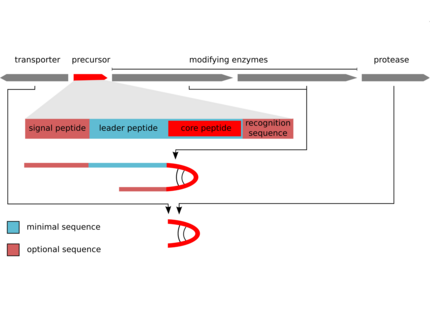
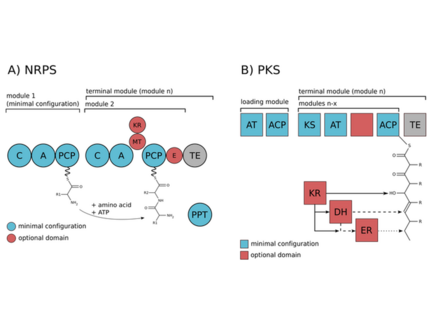
The biosynthesis of the peptides either depends on giant non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) machineries or alternatively on smaller ribosomal peptide gene clusters that use posttranslational modification enzymes to generate peptides of great complexity (RiPPs).We could assign non-ribosomal pathways to the potent cyanobacterial toxin microcystin and the protease inhibitor aeruginosin and ribosomal pathways to the cyanobacterial peptides microcyclamide, and microviridin.
Both non-ribosomal peptide synthetases and ribosomal peptide synthesis system have great potential for synthetic biology approaches. Biochemical and bioinformatic approaches can guide manipulation of peptides; as the natural pathways are shuffled in a process of perpetual chemical innovations. Analysis of natural recombination events can thus provide lessons for combinatorial biochemistry approaches.
Collaborations
Keishi Ishida,Christian Hertweck, HKI Jena
Roderich Süßmuth, TU Berlin
Holger Jenke-Kodama, OIST Okinawa
Publications
Pancrace, C., Ishida, K., Briand, E., Gatte-Picchi, D., Weiz, A.R., Guljamow, A., Scalvenzi, T., Sassoon, N., Hertweck, C., Dittmann, E.*, Gugger, M.* (2018) A unique biosynthetic pathway in bloom-forming cyanobacterial genus Microcystis jointly assembles cytotoxic aeruginoguanidines and microguanidines. ACS Chem. Biol. , in press.
Meyer, S., Mainz, A., Kehr, J.C., Suessmuth, R.D., Dittmann, E. (2017) Prerequisites of isopeptide bond formation in microcystin biosynthesis. ChemBioChem 18: 2376-2379.
Ahmed, M.N., Reyna-González, E., Schmid, B., Wiebach, V., Suessmuth, R.D., Dittmann, E.*, Fewer, D.* (2017) Phylogenomic analysis of the microviridin biosynthetic pathway coupled with targeted chemoenzymatic synthesis yields potent protease inhibitors. ACS Chem. Biol. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b00124
Reyna-González, E., Schmid, B., Petras, D., Süssmuth, R.D., Dittmann, E. (2016) Leader peptide-free in vitro reconstitution of microviridin biosynthesis enables design of synthetic protease-targeted libraries. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 55: 9398-9401.
Meyer, S., Kehr, J-C., Mainz, A., Dehm, D., Petras, D., Süssmuth, R.D., Dittmann, E. (2016) Biochemical dissection of the natural diversification of microcystin provides lessons for synthetic biology of NRPS. Cell Chem. Biol. 23:462-471.
Dittmann, E., Gugger, M., Sivonen, K., Fewer, D. (2015) Natural product biosynthetic diversity and comparative genomics of the cyanobacteria. Trends Microbiol. 23: 642-652.
Gatte-Picchi, D., Weiz, A., Ishida, K., Hertweck, C., Dittmann, E. (2014) Functional analysis of environmental DNA derived miroviridins provides new insights into the
diversity of the tricyclic peptide family. Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 80:1380-1387.
Weiz, A., Ishida, K., Quitterer, F., Meyer, S., Müller, K., Groll, M., Hertweck, C., Dittmann, E. (2014) Harnessing the evolvability of tricyclic microviridins to dissect protease-inhibitor interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53: 3735-3738.
van der Donk, W.A. et al. (2013) Ribosomally synthesized and posttranslationally modified peptide natural products: overview and recommendations for a universal nomenclature. Nat. Prod. Rep. 30: 108-160.
Welker, M., Dittmann, E., von Döhren, H. (2012) Cyanobacteria as source for natural products. Meth. Enzymol. 517:23-46.
Kehr, J.C., Gatte-Picchi, D., Dittmann, E. (2011) Natural product biosyntheses in cyanobacteria: A treasure trove of unique enzymes. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 7: 1622-1635.
Weiz, A., Ishida, K., Makower, K., Ziemert, N., Hertweck, C., Dittmann, E. (2011) Leader peptide and a membrane protein scaffold guide the biosynthesis of tricyclic depsipeptides in cyanobacteria. Chem. Biol. 18: 1413-1421.
Ziemert, N., Ishida, K., Weiz, A., Hertweck, C., Dittmann, E. (2010) Exploiting the natural diversity of microviridin gene clusters for the discovery of novel tricyclic depsipeptides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 76:3568-3574.
Jenke-Kodama, H., Dittmann, E. (2009) Evolution of metabolic diversity: Insights from microbial polyketide synthases. Phytochem. 70:1858-1866.
Jenke-Kodama, H., Dittmann, E. (2009) Bioinformatic perspectives on NRPS/PKS megasynthases: Advances and challenges. Nat. Prod. Rep. 26:874-883.
Ishida, K., Welker, M., Christiansen, G., Cadel-Six, S., Bouchier, C., Dittmann, E., Hertweck, C., Tandeau de Marsac, N. (2009) Plasticity and evolution of aeruginosin biosynthesis in cyanobacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75: 2017-2026.
Ziemert, N., Ishida, K., Liaimer, A., Hertweck, C., Dittmann, E. (2008) Ribosomal synthesis of tricyclic depsipeptides in bloom-forming cyanobacteria. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 47: 7756-7759.
Ziemert, N., Ishida, K., Quillardet, P., Bouchier, C., Hertweck, C., Tandeau de Marsac, N., Dittmann, E. (2008) Microcyclamide biosynthesis in two strains of Microcystis aeruginosa: from structure to genes and vice versa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 74: 1791-1797.
Nguyen, T., Ishida, K., Jenke-Kodama, H., Dittmann, E., Gurgui, C., Hochmuth, T., Taudien, S., Platzer, M., Hertweck, C., Piel, J. (2008) Exploiting the mosaic structure of trans-acyltransferase polyketide synthases for natural product discovery and pathway dissection. Nat. Biotechnol. 26: 225-233.
Jenke-Kodama, H., Müller, R., Dittmann, E. (2008) Evolutionary Mechanisms underlying secondary metabolite diversity. In: Petersen, F. and Amstutz, R. (Eds) Progress in Drug Research. Vol. 65, pp. 119-141.
Traitcheva, N., Jenke-Kodama, H., He, J., Dittmann, E., Hertweck, C. (2007) Non-Colinear Polyketide Biosynthesis in the Aureothin and Neoaureothin Pathways: An Evolutionary Perspective. Chembiochem. 8: 1841-1849
Ishida, K., Christiansen, G., Yoshida, W., Welker, M., Hertweck, C., Bonjoch, J., Börner,T., Hemscheidt, T., Dittmann, E. (2007). Biosynthetic pathway and structure analysis of aeruginoside 126A and B, cyanobacterial peptides bearing an unusual 2-carboxy-6-hydroxyoctahydroindole moiety. Chem. Biol. 14: 565-576.
Sandmann, A., Dickschat, J., Jenke-Kodama, H., Kunze, B., Dittmann, E., and Müller, R. (2007) A type II polyketide synthase from the Gram negative bacterium Stigmatella aurantiaca is involved in aurachin alkaloid biosynthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 46: 2712-2716.
Jenke-Kodama, H., Börner, T., Dittmann, E. (2006) Natural Biocombinatorics in the Polyketide Synthase Genes of the Actinobacterium Streptomyces avermitilis. PLoS Comp. Biol. 2:e132
Gross, F., Luniak, N., Gottschalk, D., Perlova, O., Gaitatzis, N., Gerth, K., Jenke-Kodama, H., Dittmann, E. and Müller, R. (2006) Bacterial type III polyketide synthases: Phylogenetic analysis and potential for the production of novel secondary metabolites by heterologous expression in Pseudomonads. Arch. Microbiol. 185: 28-38.
Jenke-Kodama, H., Sandmann, A., Müller, R., Dittmann, E. (2005) Evolutionary Implications of Bacterial Polyketide Synthases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 22: 2027-2039.
Sielaff H, Dittmann E, Tandeau De Marsac N, Bouchier C, Von Döhren H, Börner T, Schwecke T. (2003) The mcyF gene of the microcystin biosynthetic gene cluster fromMicrocystis aeruginosa encodes an aspartate racemase. Biochem J. 373: 909-916.
Christiansen, G., Fastner, J., Erhard, M., Börner, T., Dittmann, E. (2003) Microcystin biosynthesis in Planktothrix: genes, evolution and manipulation. J Bacteriol. 185: 564-572.
Tillett, D. Dittmann, E., Erhard, M., von Döhren, H, Börner, T., Neilan, B.A. (2000) Structural organization of microcystin biosynthesis in Microcystis aeruginosa PCC7806: An integrated peptide-polyketide synthetase system. Chem. Biol. 7:753-764
Dittmann, E., Neilan, B. A., Erhard, M., von Döhren, H., Börner, T. (1997) Insertional mutagenesis of a peptide synthetase gene that is responsible for hepatotoxin production inMicrocystis aeruginosa PCC 7806, Mol. Microbiol. 26: 779-784